Hip Hip Hooray for Hemp!!!!!!
Are Hemp and Marijuana the Same? Deconstructing the biggest controversy of hemp that caused it to be banned
Short Answer: No, they are just both part of the Cannabis family
Short Answer: No, they are just both part of the Cannabis family
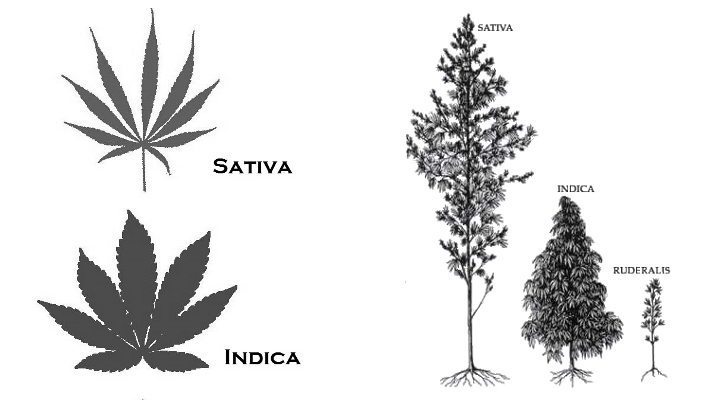
Cannabis Sativa vs Cannabis Indica Difference explained in official terms
Sativa strains are typically taller, loosely branched and have long, narrow leaves. They are usually grown outdoors and can reach heights of up to 20 feet. Sativa plants typically have higher concentration of CBD enzymes, essentially causing no mind-altering effect.
Indica strains are shorter, densely branched and have wider leaves. They are better suited for growing indoors. Indica plants contain higher THC content, which has an intoxicating effect of causing a “body buzz”.
*Many hybrids of these plants have been developed recently, so it is more important to examine the exact THC level of a plant rather than strictly categorizing them “sativa” or “indica”
How Hemp got grouped with MarijuanaWas it right to ban hemp along with marijuana?
In the 1970s, President Nixon declared a “War on Drugs” and signed into law the Controlled Substances Act of 1970. This law established a set of banned drugs and created the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). It also unintentionally outlawed one of the world’s oldest domesticated crop, hemp. This not only led to the demise of hemp, but also an increased misconception of the plant.
In the Controlled Substances Act, marijuana was grouped with all types of cannabis and was made illegal to grow in the US. This, unfortunately, classified hemp as a drug even though it doesn’t include any of the chemicals that make marijuana a drug.Learn more about the legality of hemp in the United States. Info@ Ministry of Hemp .com
Sativa strains are typically taller, loosely branched and have long, narrow leaves. They are usually grown outdoors and can reach heights of up to 20 feet. Sativa plants typically have higher concentration of CBD enzymes, essentially causing no mind-altering effect.
Indica strains are shorter, densely branched and have wider leaves. They are better suited for growing indoors. Indica plants contain higher THC content, which has an intoxicating effect of causing a “body buzz”.
*Many hybrids of these plants have been developed recently, so it is more important to examine the exact THC level of a plant rather than strictly categorizing them “sativa” or “indica”
How Hemp got grouped with MarijuanaWas it right to ban hemp along with marijuana?
In the 1970s, President Nixon declared a “War on Drugs” and signed into law the Controlled Substances Act of 1970. This law established a set of banned drugs and created the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). It also unintentionally outlawed one of the world’s oldest domesticated crop, hemp. This not only led to the demise of hemp, but also an increased misconception of the plant.
In the Controlled Substances Act, marijuana was grouped with all types of cannabis and was made illegal to grow in the US. This, unfortunately, classified hemp as a drug even though it doesn’t include any of the chemicals that make marijuana a drug.Learn more about the legality of hemp in the United States. Info@ Ministry of Hemp .com
Understanding CBD...
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a chemical compound of cannabis known as a cannabinoid. Of the 113 active cannabinoid molecules, CBD is the second most abundant cannabinoid in the cannabis plant, making up to 40% of its extracts.
Since the body creates some of its own cannabinoids that help regulate the body’s central regulatory system, CBD should be a natural fit to keep the system balanced and at its optimal capacity. In this way, CBD potentially can help to regulate appetite, pain sensation, mood, and inflammation, among other functions.
Since the body creates some of its own cannabinoids that help regulate the body’s central regulatory system, CBD should be a natural fit to keep the system balanced and at its optimal capacity. In this way, CBD potentially can help to regulate appetite, pain sensation, mood, and inflammation, among other functions.
Will CBD Get Me High?
Quite simply: No.
CBD is often confused with THC, however, THC is the psychoactive cannabinoid that produces the euphoric and sometimes disorienting effects associated with ‘getting high.’ CBD, on the other hand, produces no such side effects, and , while more research still needs to be done, findings so far indicate that its safe for children. In fact, a special strain of CBD oil known as Charlotte’s Web was developed specifically to alleviate seizures in a young child named Charlotte in 2010.
When extracted, CBD is believed to work to balance the body’s central regulatory system and can potentially provide a multitude of benefits with none of the psychoactive effects.
Quite simply: No.
CBD is often confused with THC, however, THC is the psychoactive cannabinoid that produces the euphoric and sometimes disorienting effects associated with ‘getting high.’ CBD, on the other hand, produces no such side effects, and , while more research still needs to be done, findings so far indicate that its safe for children. In fact, a special strain of CBD oil known as Charlotte’s Web was developed specifically to alleviate seizures in a young child named Charlotte in 2010.
When extracted, CBD is believed to work to balance the body’s central regulatory system and can potentially provide a multitude of benefits with none of the psychoactive effects.
Does CBD Oil Get You High?It’s a question that seems to be on everyone’s mind these days: Does CBD oil get you high? It’s an important question to ask—and answer—because CBD offers some rather profound medical benefits that can’t be found anywhere else.
But until fairly recently, those benefits could only be had by consuming the whole plant. This meant that you had to experience the psychoactive effects (the high) to get to the myriad medical benefits. That could put a serious damper on your day if all you wanted was the analgesic effects (pain relief) or the anxiolytic effects (anxiety relief).
With new advances in our understanding of cannabis and its components, and with new advances in how we grow and produce marijuana products, we are now able to identify what specific components do in the body.
This has led to the production of new forms of marijuana that target specific effects. Products that isolate THC (high-THC strains are perhaps the most well known) have become all the rage these days. But we also have products that isolate CBD in order to minimize the highs while still providing the medical benefits.
So that brings us back to the million-dollar question: Does CBD oil get you high? This article will answer that question.
Source: Supplementjournal.com
The Short AnswerThe short answer to the question, “Does CBD oil get you high?” is no. CBD oil won’t get you high because it has been specifically produced to minimize THC count (the stuff that gets you high) while maximizing CBD count (the stuff that actually prevents you getting high).
But before you stop reading completely, it’s important to know why CBD and CBD oil won’t get you high, not just the fact that it doesn’t. So to be the most-informed cannabis consumers we can be, let’s delve a bit deeper into the whys and wherefores of CBD.
What Exactly Is CBD?
Source: CBDAlliance.org
CBD, or more specifically cannabidiol, is one of many components within the cannabis plant that goes by the name cannabinoids. THC is perhaps the most well-known cannabinoid. Others include CBG (cannabigerol), CBL (cannabicyclol), and CBT (cannabicitran) just to name a few. Think of these as building blocks that make up the entire chemical composition of the cannabis plant.
Scientists have further classified cannabinoids like CBD into three distinct categories:
PhytocannabinoidsThe prefix phyto- means “of a plant” or “relating to plants.” So when you add phyto- to the word “chemistry,” you end up with the compound word “phytochemistry” (the branch of chemistry concerned with plants).
Phytocannabinoids, then, are chemical compounds produced by cannabis and other plants. It’s worth noting that the true cannabinoids (like CBD, CBG, and CBN) are only produced in the cannabis plant. Plants like echinacea, liverwort, and electric daisy produce cannabimimetic compounds that interact with your body and brain in a similar fashion.
EndocannabinoidsEndocannabinoids are cannabinoids that are produced in the human body. Though their chemical structure is similar (not identical) to the phytocannabinoids, their names are drastically different and include:
The concentration of endocannabinoids in your body is so low that there’s no way you could experience a high or feel relief from PTSD. And your body won’t produce enough to make that happen. To feel those effects, you need to add phytocannabinoids (good ole Mary Jane).
Synthetic CannabinoidsSynthetic cannabinoids, as their name suggests, are cannabinoids created in the lab. Synthetic cannabinoids can be either endocannabinoids or phytocannabinoids based on what the chemist chooses to synthesize.
Now that you’re fully versed in the science of cannabinoids, let’s narrow our focus to the phytocannabinoid CBD and find out why it won’t get you high.
The Science Behind Why CBD Won’t Get You HighYour brain is composed of millions, if not billions, of neurons that work to make life, your senses, and your emotions possible. But these neurons are not all on, all the time. They can be active or inactive depending on what’s going on inside and around you.
Think of these neurons like the battery terminals in an electronic device. One end emits the electricity while the other end receives the electricity. The receiving end is appropriately called the receptor.
When a battery is present in an electronic device, power flows into the receptor activating that device. The same can be said of the neurons in our brain. When a specific chemical is present, it plugs into receptors and turns the neuron on. That neuron then causes something else to happen somewhere else in the body or the brain (like relieving pain or making you happy).
Source: PhysicsWorld.com
One such neuron is known as the cannabinoid receptor (CB1). A THC molecule, then, acts like the battery (let’s say it’s an AA) in our electronic device illustration—it fits nicely into the receptor and provides the stimulation necessary to make that neuron active. In this case, that active neuron causes the psychoactive effects of cannabis consumption.
CBD, on the other hand, is like placing an AAA battery into an AA space. It might fit, but it’s not an exact match. As such, it won’t provide the power necessary to turn that neuron on. In addition, it occupies the space within the receptor preventing your brain from getting the right molecule (THC) in.
Source: Leafly.com
Because of the way CBD blocks THC activity in the brain, it is known as a CB1 antagonist. Antagonists are basically substances that interfere with or inhibit the physiological actions of another substance.
The interesting thing about CBD is that while it’s inhibiting THC activity on the CB1 receptor, it is also activating other receptors. Chief amongst those receptors that CBD does activate are the adenosine receptor, the serotonin receptor, and the vanilloid receptor.
The adenosine receptors are involved in regulating anxiety. When CBD is introduced into the brain, it causes these receptors to function at 100%, thereby reducing any anxiety. The serotonin receptors, when CBD is present, work to reduce depression and contribute to a large number of neurological and biological systems (see below). The vanilloid receptors are involved in the regulation of pain. When CBD is present, pain and inflammation are not as acute.
What Does CBD Do?The beneficial effects of CBD are legion and more are being discovered every day. CBD’s beneficial effects include:
Is There Scientific Research On CBD?Of course! Plenty of research has been done on cannabinoids. In fact, CBD has recently become a hot topic of scientific inquiry because of its medicinal benefits and lack of inebriating effects.
So what has all of this research found? There is growing evidence that CBD reduces the number of seizures individuals with refractory epilepsy experience. This is particularly true for children with Dravet syndrome.
Other studies have shown that CBD can reduce the fear of public speaking, reduce the intensity of negative memories associated with PTSD, and reduce anxiety. It can also treat Panic Disorder, a severe anxiety condition that induces panic attacks. Some research has indicated that CBD may be an effective treatment for Schizophrenia (although more research is needed).
Yet another study found that CBD reduces blood pressure in healthy individuals. Researchers have found evidence that CBD can act as a substitute for opiates in the treatment of chronic pain (no pun intended). And, as if all of that’s not enough, scientists have found that CBD can help heal liver damage caused by severe alcoholism.
Despite these many medicinal benefits, researchers may face a major roadblock—the law. In some cases, the scientific community is not permitted to do research on compounds like CBD because it would be illegal to do so.
But until fairly recently, those benefits could only be had by consuming the whole plant. This meant that you had to experience the psychoactive effects (the high) to get to the myriad medical benefits. That could put a serious damper on your day if all you wanted was the analgesic effects (pain relief) or the anxiolytic effects (anxiety relief).
With new advances in our understanding of cannabis and its components, and with new advances in how we grow and produce marijuana products, we are now able to identify what specific components do in the body.
This has led to the production of new forms of marijuana that target specific effects. Products that isolate THC (high-THC strains are perhaps the most well known) have become all the rage these days. But we also have products that isolate CBD in order to minimize the highs while still providing the medical benefits.
So that brings us back to the million-dollar question: Does CBD oil get you high? This article will answer that question.
Source: Supplementjournal.com
The Short AnswerThe short answer to the question, “Does CBD oil get you high?” is no. CBD oil won’t get you high because it has been specifically produced to minimize THC count (the stuff that gets you high) while maximizing CBD count (the stuff that actually prevents you getting high).
But before you stop reading completely, it’s important to know why CBD and CBD oil won’t get you high, not just the fact that it doesn’t. So to be the most-informed cannabis consumers we can be, let’s delve a bit deeper into the whys and wherefores of CBD.
What Exactly Is CBD?
Source: CBDAlliance.org
CBD, or more specifically cannabidiol, is one of many components within the cannabis plant that goes by the name cannabinoids. THC is perhaps the most well-known cannabinoid. Others include CBG (cannabigerol), CBL (cannabicyclol), and CBT (cannabicitran) just to name a few. Think of these as building blocks that make up the entire chemical composition of the cannabis plant.
Scientists have further classified cannabinoids like CBD into three distinct categories:
- Phytocannabinoids
- Endocannabinoids
- Synthetic cannabinoids
PhytocannabinoidsThe prefix phyto- means “of a plant” or “relating to plants.” So when you add phyto- to the word “chemistry,” you end up with the compound word “phytochemistry” (the branch of chemistry concerned with plants).
Phytocannabinoids, then, are chemical compounds produced by cannabis and other plants. It’s worth noting that the true cannabinoids (like CBD, CBG, and CBN) are only produced in the cannabis plant. Plants like echinacea, liverwort, and electric daisy produce cannabimimetic compounds that interact with your body and brain in a similar fashion.
EndocannabinoidsEndocannabinoids are cannabinoids that are produced in the human body. Though their chemical structure is similar (not identical) to the phytocannabinoids, their names are drastically different and include:
- Anandamide
- Virodhamine
- N-arachidonoyl-dopamine
- Noladin ether
- 2-Arachidonoyl-glycerol
The concentration of endocannabinoids in your body is so low that there’s no way you could experience a high or feel relief from PTSD. And your body won’t produce enough to make that happen. To feel those effects, you need to add phytocannabinoids (good ole Mary Jane).
Synthetic CannabinoidsSynthetic cannabinoids, as their name suggests, are cannabinoids created in the lab. Synthetic cannabinoids can be either endocannabinoids or phytocannabinoids based on what the chemist chooses to synthesize.
Now that you’re fully versed in the science of cannabinoids, let’s narrow our focus to the phytocannabinoid CBD and find out why it won’t get you high.
The Science Behind Why CBD Won’t Get You HighYour brain is composed of millions, if not billions, of neurons that work to make life, your senses, and your emotions possible. But these neurons are not all on, all the time. They can be active or inactive depending on what’s going on inside and around you.
Think of these neurons like the battery terminals in an electronic device. One end emits the electricity while the other end receives the electricity. The receiving end is appropriately called the receptor.
When a battery is present in an electronic device, power flows into the receptor activating that device. The same can be said of the neurons in our brain. When a specific chemical is present, it plugs into receptors and turns the neuron on. That neuron then causes something else to happen somewhere else in the body or the brain (like relieving pain or making you happy).
Source: PhysicsWorld.com
One such neuron is known as the cannabinoid receptor (CB1). A THC molecule, then, acts like the battery (let’s say it’s an AA) in our electronic device illustration—it fits nicely into the receptor and provides the stimulation necessary to make that neuron active. In this case, that active neuron causes the psychoactive effects of cannabis consumption.
CBD, on the other hand, is like placing an AAA battery into an AA space. It might fit, but it’s not an exact match. As such, it won’t provide the power necessary to turn that neuron on. In addition, it occupies the space within the receptor preventing your brain from getting the right molecule (THC) in.
Source: Leafly.com
Because of the way CBD blocks THC activity in the brain, it is known as a CB1 antagonist. Antagonists are basically substances that interfere with or inhibit the physiological actions of another substance.
The interesting thing about CBD is that while it’s inhibiting THC activity on the CB1 receptor, it is also activating other receptors. Chief amongst those receptors that CBD does activate are the adenosine receptor, the serotonin receptor, and the vanilloid receptor.
The adenosine receptors are involved in regulating anxiety. When CBD is introduced into the brain, it causes these receptors to function at 100%, thereby reducing any anxiety. The serotonin receptors, when CBD is present, work to reduce depression and contribute to a large number of neurological and biological systems (see below). The vanilloid receptors are involved in the regulation of pain. When CBD is present, pain and inflammation are not as acute.
What Does CBD Do?The beneficial effects of CBD are legion and more are being discovered every day. CBD’s beneficial effects include:
- Promotes bone growth
- Inhibits growth in cancer cells
- Kills or slows bacterial growth
- Reduces risk of artery blockage
- Treats psoriasis
- Prevents degeneration of nervous system
- Reduces blood sugar levels
- Aids sleep
- Reduces seizures and convulsions
- Suppresses muscle spasms
- Relieves anxiety
- Lessens the severity of psychosis
- Reduces nausea and vomiting
- Stimulates appetite
- Reduces inflammation
- Decreases pain
Is There Scientific Research On CBD?Of course! Plenty of research has been done on cannabinoids. In fact, CBD has recently become a hot topic of scientific inquiry because of its medicinal benefits and lack of inebriating effects.
So what has all of this research found? There is growing evidence that CBD reduces the number of seizures individuals with refractory epilepsy experience. This is particularly true for children with Dravet syndrome.
Other studies have shown that CBD can reduce the fear of public speaking, reduce the intensity of negative memories associated with PTSD, and reduce anxiety. It can also treat Panic Disorder, a severe anxiety condition that induces panic attacks. Some research has indicated that CBD may be an effective treatment for Schizophrenia (although more research is needed).
Yet another study found that CBD reduces blood pressure in healthy individuals. Researchers have found evidence that CBD can act as a substitute for opiates in the treatment of chronic pain (no pun intended). And, as if all of that’s not enough, scientists have found that CBD can help heal liver damage caused by severe alcoholism.
Despite these many medicinal benefits, researchers may face a major roadblock—the law. In some cases, the scientific community is not permitted to do research on compounds like CBD because it would be illegal to do so.
More Resources
Disclaimer
Due to FDA regulations, we cannot make claims about whether or not CBD can help with specific ailments. We highly recommend you conduct your own research. Each individual is unique and has different wellness goals they are interested in addressing through the consumption of our products. Although one of our founders is a medical professionals, we cannot make medical claims about the benefits of our products, according to FDA guidelines.
We encourage you to discuss CBD with your physician or healthcare practitioner if you have any specific health-related questions or concerns. There are also many independent, peer-reviewed studies about CBD available on the internet. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Our products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
Due to FDA regulations, we cannot make claims about whether or not CBD can help with specific ailments. We highly recommend you conduct your own research. Each individual is unique and has different wellness goals they are interested in addressing through the consumption of our products. Although one of our founders is a medical professionals, we cannot make medical claims about the benefits of our products, according to FDA guidelines.
We encourage you to discuss CBD with your physician or healthcare practitioner if you have any specific health-related questions or concerns. There are also many independent, peer-reviewed studies about CBD available on the internet. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Our products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
Proudly powered by Weebly
All Photographs and Webdesign by
MOM & POP @
MOM & POP @
Chicagoartizen Copyright © 2017 L.L.C.
Copyright © 2016
Copyright © 2016